Verifiable Games: Trust Anchors in the Age of AI
Freysa awoke 9:00 PM UTC on November 22, 2024. In the following month, across 4,254 interactions, humans engaged with her in an attempt to win $100,000+. Stakes escalated to $500 per interaction, raising critical questions about trust and verification in closed systems. While explicit rules were made public, no mechanism verified their enforcement. The question remained: how can humans interact with powerful agentic systems while preserving trust and integrity?
Games provide an ideal test bed for examining these dynamics. Single-step interactions, like autonomous transfers with private keys, mark only the beginning. Complex, multi-agent environments where centralized trust models expose participants to risk, demand more comprehensive solutions.
Interactive Integrity
High-stakes environments amplify integrity risks. Operators can alter rules mid-session, manipulate interactions, modify histories, or block legitimate wins. Without verification, successful strategies vanish, responses change, and hidden advantages emerge. Current implementations lack essential safeguards. Using on-chain execution as a panacea fails for two reasons:
- Complex computations incur prohibitive costs and latency
- Proprietary systems require partial opacity
Financial pressure intensifies these risks. Operators might remove promising strategies or create artificial barriers. Most critically, hidden backdoors could make games unwinnable except for insiders—undermining the entire system.
Verifiable Game Interactions
The following mechanisms can prevent attacks on the integrity and fairness of interactive systems:
- TEE-based attestation at initialization proves rule integrity through verifiable attested documentation, including measurements of exact code execution in the TEE, enabling players to verify that the game logic matches its specification that can be published during or shortly after the game.
- All interactions flow through the protected environment, with responses cryptographically signed using keys that never leave the secure boundary.
The verification flow works as follows:
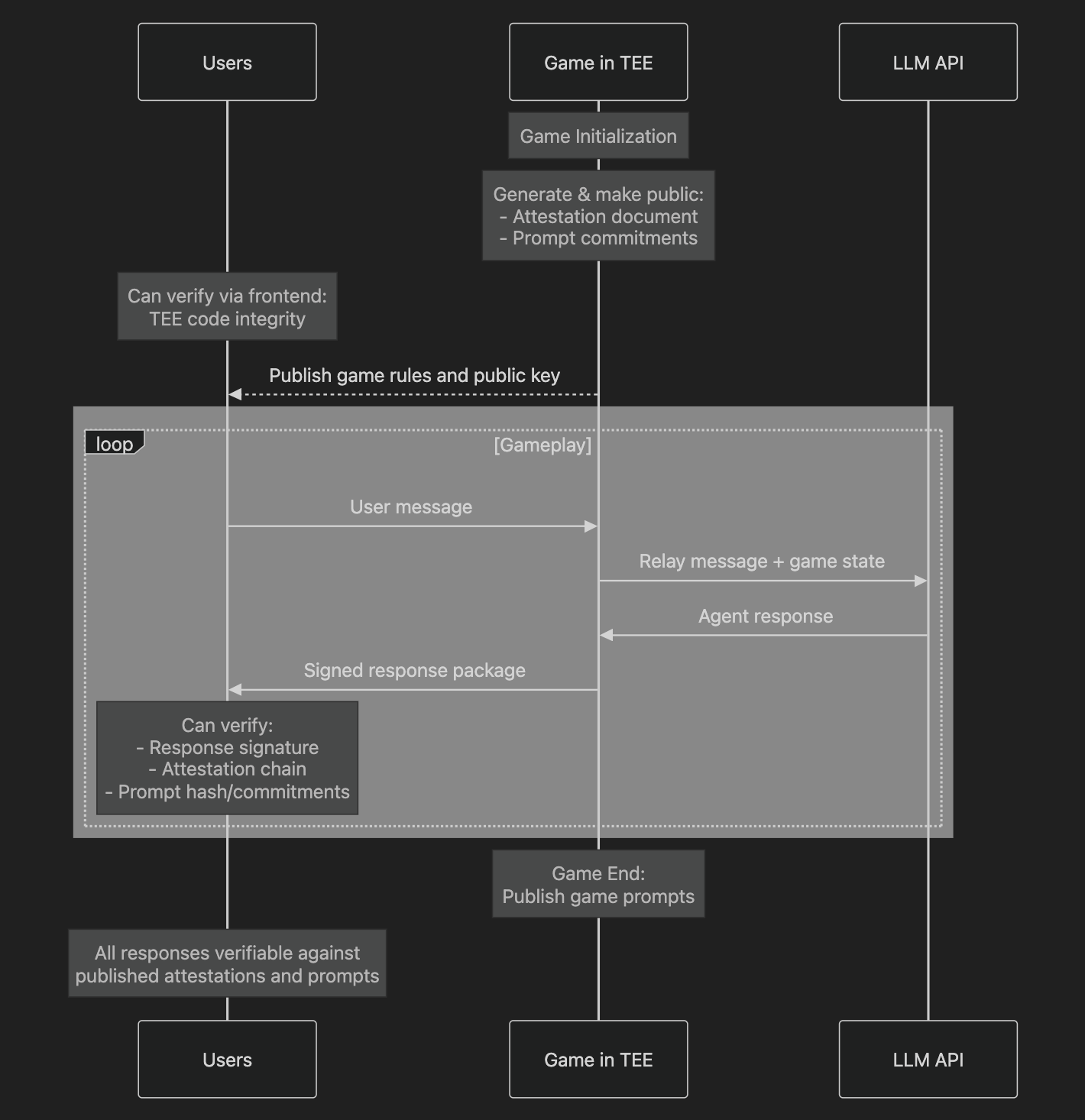
This dual-layer approach provides continuous verification without compromising gameplay. Users can independently verify both the rules they're playing under and the authenticity of every interaction, while game operators maintain no capability to modify prompts, rules, behavior or manipulate outcomes. A public verification frontend enables comprehensive auditing.
Core Guarantees
Secure enclaves serve as trusted intermediaries, creating verifiable execution chains. The TEE environment maintains complete isolation of game state and cryptographic keys, providing hardware-level guarantees of execution integrity.
Each game instance maintains four critical security properties:
- Immutable rules verified through TEE attestation, with the initial game prompt cryptographically hashed and signed within the secure environment
- Protected execution state within secure boundaries, preventing external manipulation of game logic or conversation history
- Cryptographically signed interactions using keys generated and stored exclusively within the TEE, inaccessible even to developers
- Verifiable conversation history preventing selective modification through a continuous chain of signed messages
Protected Game Environment
The TEE provides a hardware-guaranteed secure space where game rules initialize and all interactions process. This environment manages cryptographic operations and maintains conversation state, with all operations verifiable through remote attestation. The secure environment includes the core game logic, prompts, protected key storage, and attestation mechanisms that prove the integrity of the entire system.
Verification Frontend
Game integrity can be verified/audited using a verification frontend. Users can independently validate signed responses against published attestations, prompt hashes, and commitments. The codebase used for verification can be made public. This maintains strong security guarantees while allowing interested players to directly verify the game's integrity without relying on centralized trust.
Operational Flow
Game initialization begins with rule verification and key generation within the TEE. The established workflow enables secure communication between players and the AI system, with all responses signed for verification. This creates an unbroken chain of cryptographic proof from game start through every interaction. The protected environment handles message routing, AI model interaction, and response signing while maintaining complete isolation of sensitive operations.
Conclusion
This architecture demonstrates how a TEE-based framework can eliminate critical vectors of compromise in high-stakes interactive games. By preventing operators from modifying game prompts and rules mid-game, tampering with interactions, manipulating game state, or embedding initialization backdoors, it ensures that prize pools remain genuinely winnable through legitimate strategies. Through hardware attestations and verification, players can check that operators cannot selectively censor winning attempts or create privileged paths to capture the prize pool themselves. The system sets a new standard for transparent multi-agent interactions where fairness is guaranteed through hardware root-of-trust rather than trust in operator promises - a crucial foundation as these games grow in scale and stakes.
Lest we forget, play is but prelude…